ATX
Stands for "Advanced Technology eXtended."
ATX is a motherboard specification that defines the board's physical dimensions, connector placement, I/O ports, and supported power supplies. Intel introduced the ATX specification to replace the previous AT standard for desktop PCs. Several variations of the ATX have been introduced since then and are common in desktop computers.
The ATX specification introduced several significant improvements to motherboard design. It standardized the position of the I/O panel, directly integrating ports into the motherboard. It also moved the CPU and RAM slots to a location where they wouldn't interfere with full-length expansion cards. It sets requirements for compatible power supplies to include a series of connectors to provide power to the motherboard, processor, and expansion cards. It moved the connector for storage devices closer to the location of the drive bays to shorten the length of cables needed. ATX motherboards and cases also provide better airflow through the chassis than older designs.
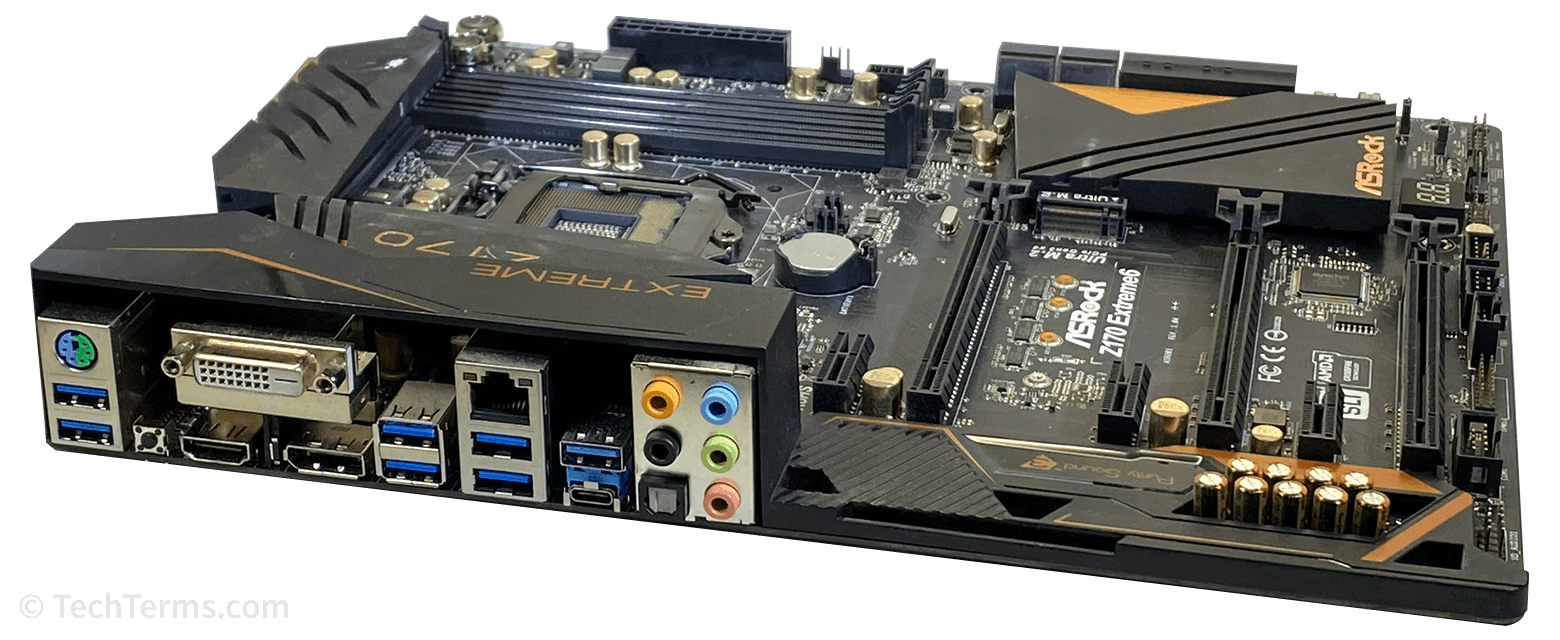
The ATX specification defines the location of the mounting holes in a computer case, so any ATX motherboard will fit in an ATX case. It also specifies several different-sized variations — some are larger to support more expansion ports, while others are smaller to fit in compact cases:
- FlexATX – 9 × 7.5 in (229 × 191 mm)
- MicroATX – 9.6 × 9.6 in (244 × 244 mm)
- ATX — 12 × 9.6 in (305 × 244 mm)
- Extended ATX (EATX) – 12 × up to 13 in (305 × up to 330 mm). Many manufacturers make motherboards smaller than the full size allowed by the standard.
NOTE: Since the different sizes use the same series of mounting holes, smaller-sized motherboards (like MicroATX) will fit in cases designed for larger ATX motherboards.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge