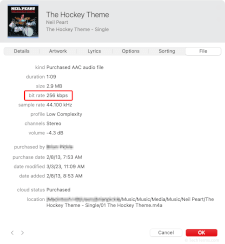
Bitrate
Bitrate is the measurement of the speed at which data is transferred or processed. It may refer to the transfer speed of a network or data connection, or to the data required per second to store and play an encoded media file. In both cases, bitrate is measured in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps).
Data Transfer
A computer network or data connection's bitrate measures the speed at which data moves from one location to another. A connection's maximum possible bitrate is known as its bandwidth. For example, a cable modem connection may let you download a file at 250 Mbps; when that finishes, you could transfer that file to an external disk over a USB connection at 600 Mbps.
Media Encoding
An audio or video file's bitrate measures how much data a file needs per second of playback. The bitrate (along with the codec used to encode it) is a standard benchmark that measures a file's quality. A higher bitrate requires less media compression, resulting in fewer compression artifacts and better dynamic range. For example, an MP3 file encoded at a bitrate of 256 Kbps will sound clearer than one encoded at 96 Kbps, since it includes more data per sample. A high-definition MP4 video encoded at 18 Mbps will look better, with fewer artifacts and more accurate colors, than one encoded at 6 Mbps.
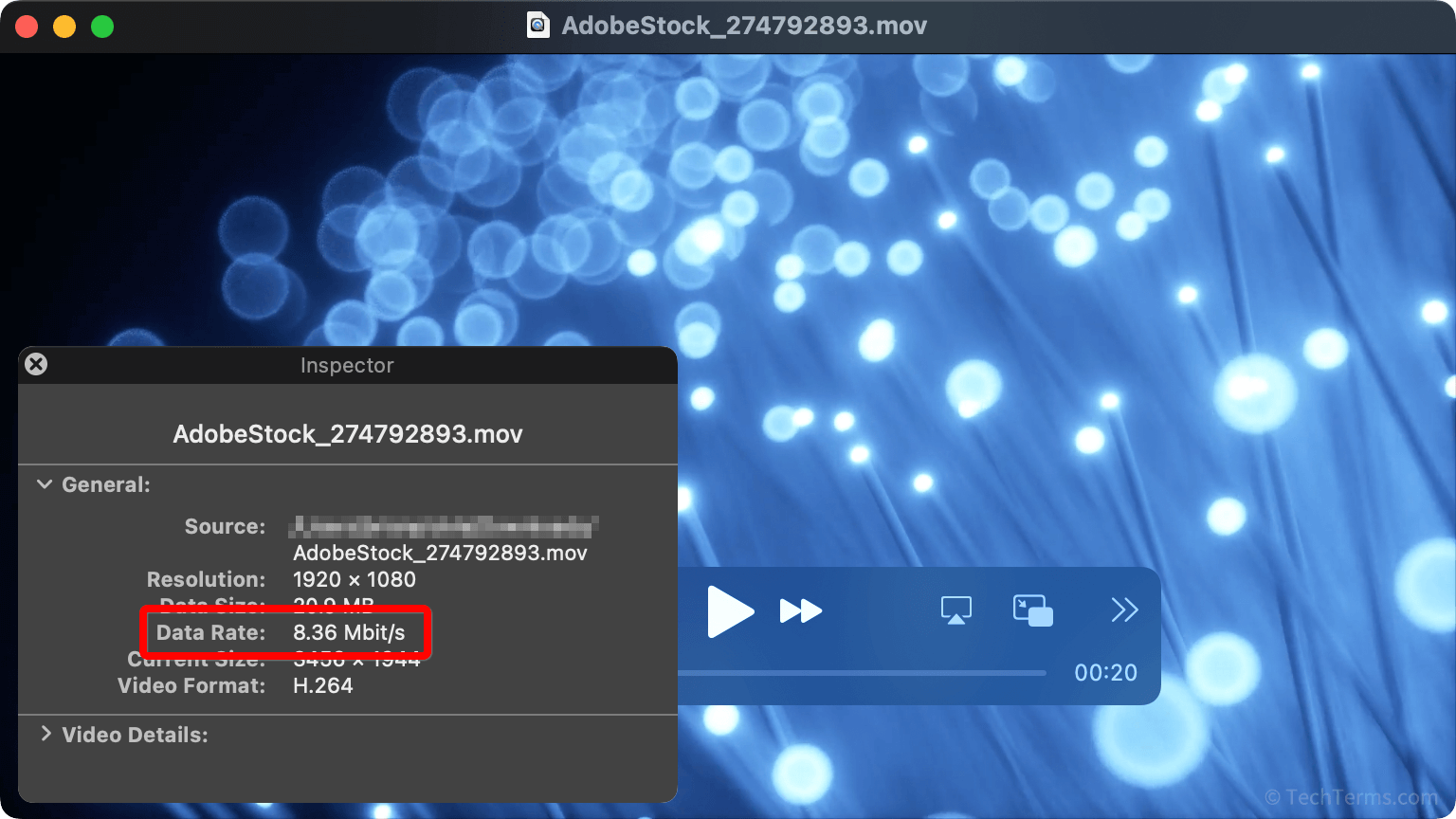
A file's bitrate is particularly important for streaming media since it determines how much network bandwidth is necessary for uninterrupted playback. Streaming media services often store several versions of a file, encoded at different bitrates. This allows them to serve higher-bitrate files to devices with faster connections and send files compressed at lower bitrates when less bandwidth is available.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge