Color Profile
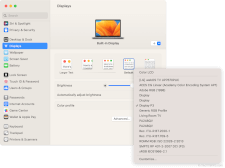
A color profile (also known as an ICC profile) is a set of configuration data that tells a computer how to display colors on a given device. Each color profile contains data about the total range of colors available (known as a gamut), and how to map color values to other standard color spaces. It may also include the performance characteristics of a specific device, like its color temperature and gamma. A computer's color management software uses color profiles to keep colors consistent between devices.
Monitors, digital cameras, scanners, and printers come with color profiles provided by their manufacturers. These profiles include specific information about how a device captures or displays colors. They are created by measuring the device using specific sample colors, calibrating its settings until the sample colors are accurate, then saving those calibration details to its profile.
While many color profiles are specific to certain devices, there are standard profiles for common color spaces. Generic color profiles for color spaces like sRGB, Adobe RGB, and LAB provide a common working profile for creating and editing digital images. When necessary, color management software converts colors from generic profiles to device-specific ones and vice versa.
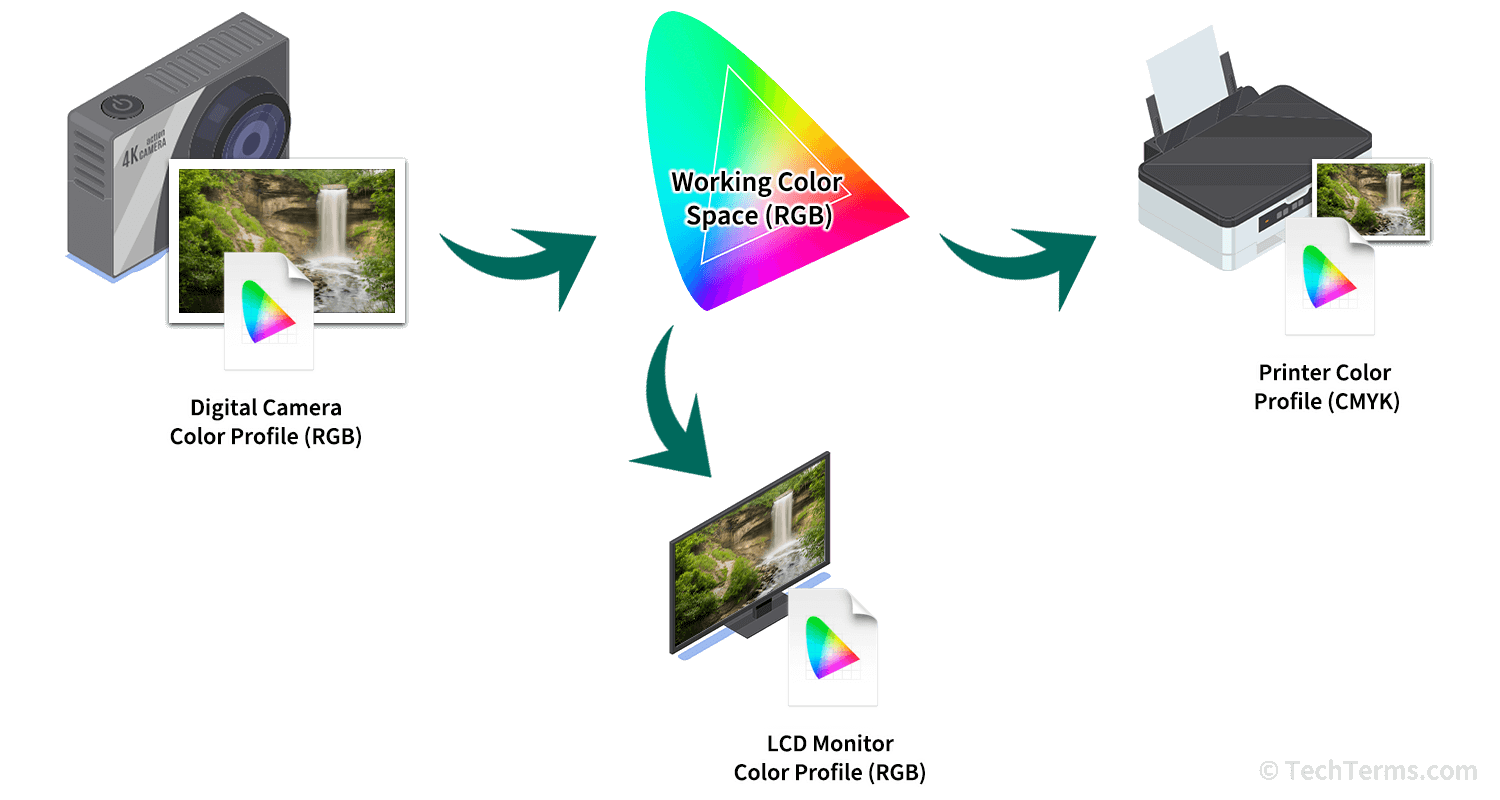
Computers translate color data between color profiles whenever an image is captured, edited, or viewed. For example, a digital camera includes its own built-in color profile based on its sensor's performance characteristics and embeds that color profile into every photograph it takes. When opened by software like Photoshop, the color management system converts colors from the embedded profile to a generic working color profile for editing, while also converting it to the monitor's color profile for display. If necessary, the software adjusts those colors to fit within the monitor's gamut while maintaining its appearance as closely as possible. Finally, when printing the photo, it is converted one more time to the printer's color profile, using color mapping tables to translate color values from RGB to CMYK.
NOTE: Camera RAW images are not given a color profile by the camera but are assigned one once imported into the photographer's editing software.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge