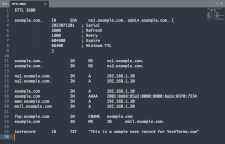
DNS Record
A DNS record is a plain text entry in a zone file that contains important information about a domain, and is an important part of the Domain Name System. A domain's zone file contains multiple DNS records that help translate human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses, including a domain's name server and mail server information. A DNS record can also include domain aliases for forwarding domains and subdomains.
Each DNS record in a zone file contains a single piece of information, which work together to provide a full set of instructions for accessing that domain and its resources. There are multiple types of DNS record that each provide different information. Some of the most common types of DNS record are listed below.
- NS records list the domain's name servers.
- A records list the domain's IPv4 address.
- AAAA records list the domain's IPv6 address.
- SOA (Start of Authority) records include authoritative information for a domain, including its primary name server and timers that instruct how often to refresh its DNS information.
- MX records list mail servers that handle email sent to the domain.
- CNAME records create aliases (or canonical names) that forward requests to another domain or subdomain.
DNS records in a zone file typically follow the same pattern, starting with the domain or hostname, followed by a record type, and then listing details for that record type. Several examples are listed below.
example.com IN NS ns1.example.com
example.com IN A 192.168.0.1
example.com IN AAAA 2001:db8:85a3::8a2e:370:7334
example.com IN MX mail.example.com
app.example.com IN CNAME web.example.com
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge