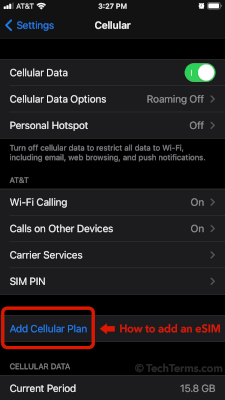
eSIM
An eSIM, short for "embedded SIM," is SIM chip or "UICC" embedded in a mobile device. It provides the same functionality as a SIM card, but is not removable.
What is a SIM?
A SIM (Subscriber Identification Module) is a unique number that identifies a device on a cellular network. When you activate a smartphone, tablet, or another device on a cellular network, the mobile provider links the SIM number to your account. When activating a smartphone, the cellular company also links the SIM to your mobile phone number.
eSIM vs SIM Card
Unlike SIM cards, which are removable and can be moved between devices, an eSIM is integrated into a device's hardware. Since eSIMs cannot be removed, they are writable and can be reprogrammed to work with different cellular providers. They can also store more than one SIM number at a single time.
Below are some advantages of eSIMs over traditional SIM cards:
- Smaller form factor - Generally, eSIMs require less than 1/3 the space of even the smallest nano-SIM cards.
- Electronically programmable - You don't need to go to a physical store or receive a new SIM card in the mail when moving to a new cellular provider. You can add the eSIM number electronically.
- Support for multiple SIMs - An eSIM makes it possible to use one device with multiple cellular providers at the same time. Common uses include separating personal and business calls and using local cellular plans when traveling internationally.
- Improved security - If your phone is lost or stolen, another person will not be able to use your SIM card.
The first smartphones to use eSIMs hit the market around 2018. Many popular models now include eSIM chips. Since embedded SIMs only work with mobile providers that support eSIM technology, many eSIM devices also have a physical SIM card slot.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge