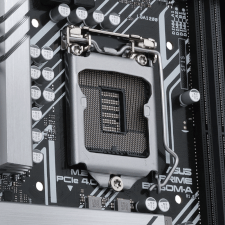
LGA
Stands for "Land Grid Array."
LGA is a type of processor package that places the connection pins in the socket on the motherboard rather than on the integrated circuit itself. The pins in the socket connect to flat contacts, or "lands," found on the bottom of the processor chip.
LGA processor packages have several advantages over pin grid array (PGA) packages. First, chips using LGA can have a much higher density of contacts than chips using PGA. The higher density allows a processor socket to take up less space on a motherboard or fit more contacts into the same area. The chips themselves are also more durable and resistant to damage since the fragile pins are instead in the socket. Finally, LGA packaging allows a processor to be either used in a socket or soldered directly to a motherboard.
There are many configurations of LGA sockets used by processor manufacturers, each in use for a few years before processor architecture changes necessitate a redesigned socket. Both Intel and AMD use varieties of LGA sockets for the CPU chips. Intel names its LGA sockets for the number of contact pins used. The first Intel LGA socket was called LGA775 (since it had 775 pins), followed by LGA1156 (which had 1,156 pins). AMD uses a sequential naming scheme that continues the pattern from their PGA sockets, first utilizing an LGA package on their TR4 and AM5 sockets.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge