LiDAR
Stands for "Light Detection and Ranging." LiDAR is a distance detection technology that uses pulses of light to detect surrounding objects. A LiDAR scanner determines the distance of each object by calculating the time each pulse takes to reflect back to the source. Using multiple light pulses, it can generate a 3D depth map of the scanned area.
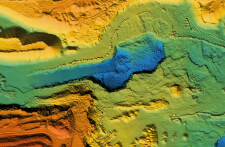
LiDAR was originally used for terrain mapping purposes, such as creating topographical images of the earth's surface. High-powered LiDAR units on drones and other aircraft can scan large areas at once. Combining LiDAR and GPS data makes it possible to generate three-dimensional maps of scanned locations.
In recent years, LiDAR has made its way to everyday devices, including automobiles and smartphones.
Automotive LiDAR
Modern cars and trucks use LiDAR to detect surrounding vehicles and other objects. Short-range LiDAR (under 50 meters) provides features like blind spot detection and park assist. Long-range LiDAR (up to 200 meters) enables features like adaptive cruise control and automatic emergency braking.
Smartphone LiDAR
Modern high-end smartphones, such as the iPhone 12 Pro and later, include short-range LiDAR. The depth-sensing technology improves photo quality and provides augmented reality (AR) features. For example, when taking a photo, LiDAR helps the phone detect and focus on the primary objects in the frame. When using AR technology, such as Snapchat filters, LiDAR improves face detection, providing smoother and more accurate mapping.
NOTE: While Apple's FaceID employs 3D imaging to detect faces, it uses infrared technology rather than LiDAR.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge