RSS
Stands for "Really Simple Syndication."
RSS is a method of publishing online content feeds using a standard XML format. Websites use RSS to provide a feed of new articles, blog posts, podcasts, and other content that gets automatically pushed to anyone subscribing to that feed. People can subscribe to RSS feeds to read articles in feed reading software and get podcasts in a podcast player.
Subscribers to an RSS feed can read articles and blog posts within a feed reader, either a standalone application or in a web browser using a browser extension. A subscriber just needs to add the RSS feed URL to the reader application, which will automatically download articles and sort them chronologically as they come in.
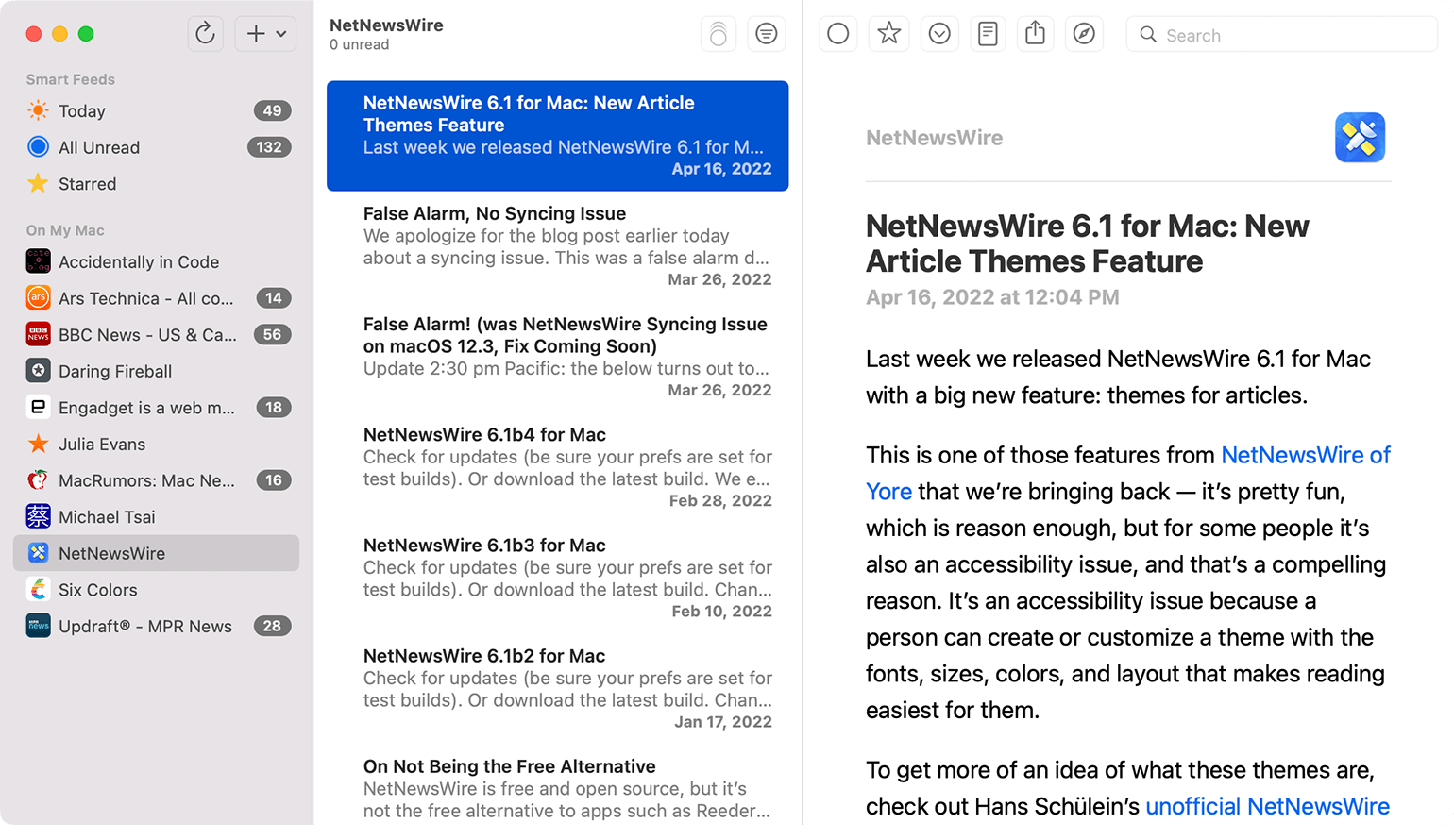
Podcasts also use RSS to distribute episodes to subscribers. Podcast player apps let listeners subscribe to a podcast by adding its RSS feed, automatically downloading new episodes as soon as they are released. The XML used by RSS includes metadata like episode titles, artwork, and show notes that provide extra information about each episode.
RSS feeds for news publishers are declining in popularity following the rise of social media. Sites like Facebook and Twitter provide both a live feed of news articles and a feed of discussion about those articles—for better or worse—which is more valuable to the publishers and advertisers.
NOTE: RDF may also stand for "RDF Site Summary," or "Rich Site Summary," but "Really Simple Syndication" is most common.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge