RUP
Stands for "Rational Unified Process."
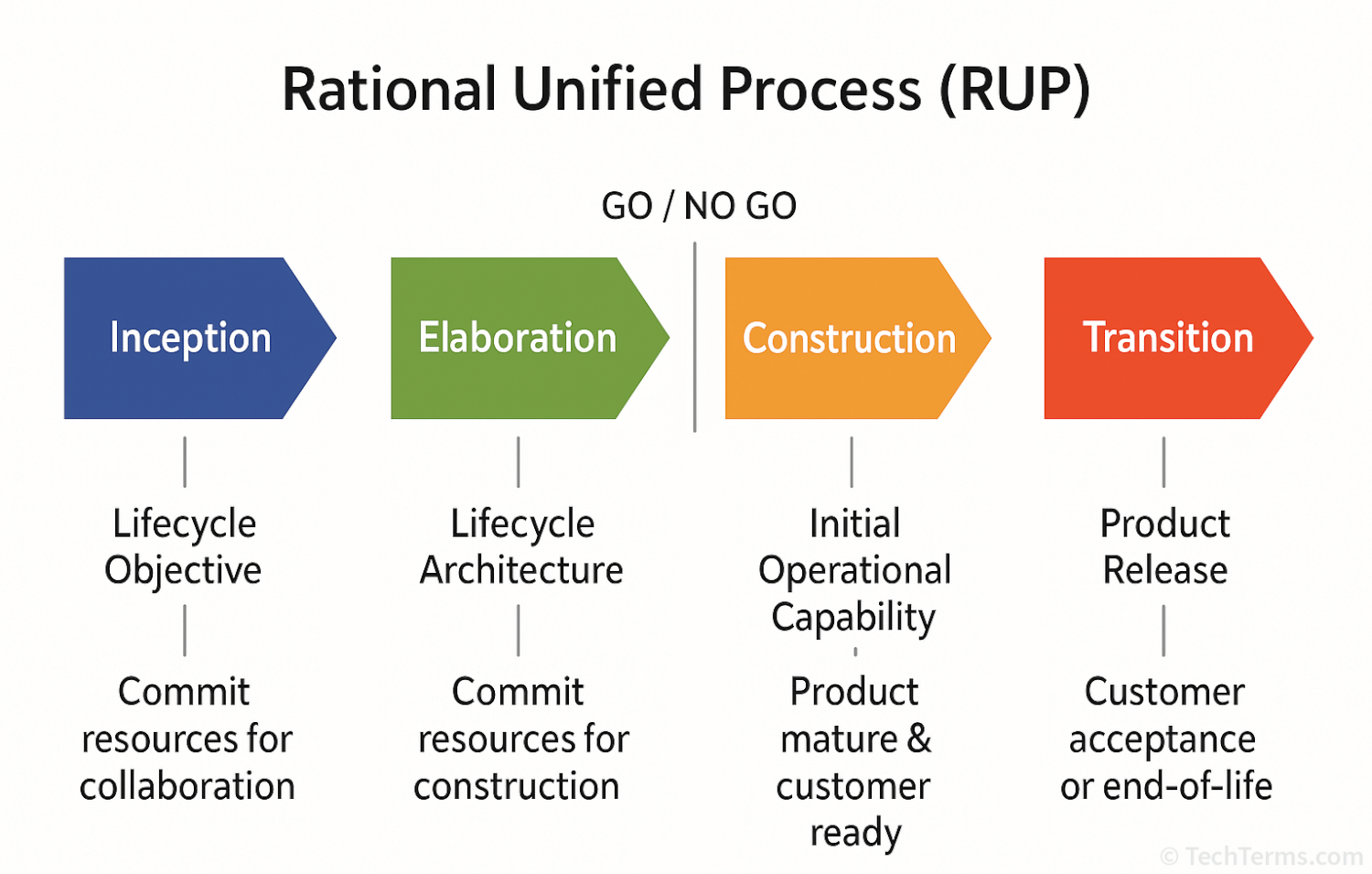
RUP is a structured software development methodology created by Rational Software, now a division of IBM. It provides a structured four-stage approach to software development. Each phase may include multiple steps, such as design, implementation, and testing.
The four phases of RUP are:
- Inception – The team defines the project's goals and scope. They evaluate whether the project is feasible and worth pursuing and identify the initial resources required.
- Elaboration – The team establishes the software's architecture and addresses key technical risks. Developers refine the project requirements and estimate the overall cost and timeline. If the project is not deemed worthwhile, it is considered "no go" and does not proceed past this stage.
- Construction – Programmers build, integrate, and thoroughly test the application to meet the defined requirements. The bulk of the development takes place in this step.
- Transition – The company releases the finished product to users. They collect feedback and make final refinements or bug fixes to ensure a smooth deployment.
RUP provides a disciplined approach to software development, helping teams manage complex projects and align development with business goals. The structured framework helps reduce risks, control costs, and improve the predictability of software projects.
RUP Today
While RUP was widely adopted in the late 1990s and early 2000s, its usage has declined in favor of more lightweight and flexible methodologies such as Agile and Scrum. However, some organizations still use RUP, especially for large-scale projects that benefit from a formalized process. Additionally, aspects of RUP — such as iterative development and risk management — have influenced many modern development practices. Software companies sometimes adopt a hybrid approach, combining RUP principles with Agile methods.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge