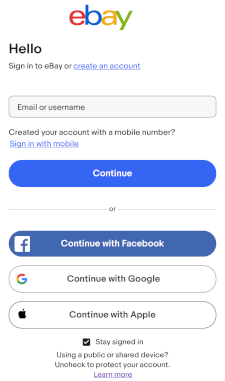
SSO
Stands for "Single Sign-On."
SSO is an authentication method that allows a person to use a single set of login credentials for multiple websites or services. Using SSO minimizes the number of times a user has to log in and the number of passwords they need to remember. SSO is often used alongside multi-factor authentication (MFA) or two-factor authentication (2FA) to increase the level of security used for the single set of credentials.
Developers of software applications and web apps can choose to build support for an SSO method into their apps. Google, Apple, and Facebook all provide SSO services for individuals, allowing someone to sign in to a new app or website without creating a separate account for it. Several other companies provide SSO products focused on the more robust needs of large businesses.
Logging in via SSO requires that all the services support a common identity provider. When the user first logs in to one of the services, it passes the sign-on process to the identity provider. After the user signs in with their username and password, the identity provider creates an authentication token establishing the user's credentials and stores that token in the user's web browser or the identity provider's server. When the user tries to access another service that supports the same SSO method, the service checks the token (in the web browser or on the identity provider's server) and, if successful, grants the user access.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge