Subpixel
A subpixel is a subdivision of a single pixel on a screen. It generally refers to one of the three RGB elements of a single pixel.
Computer monitors, televisions, and smartphone and tablet screens show images on a large grid of pixels. Each of those pixels consists of several subpixels that individually light up in a specific color—red, green, or blue, collectively referred to as RGB (some OLED displays use an additional white subpixel for extra brightness). If all of a pixel's subpixels light up to 100%, the pixel will appear white; if they're all turned off to 0%, it will appear black. By lighting up these subpixels to different levels, a screen can show millions of colors.
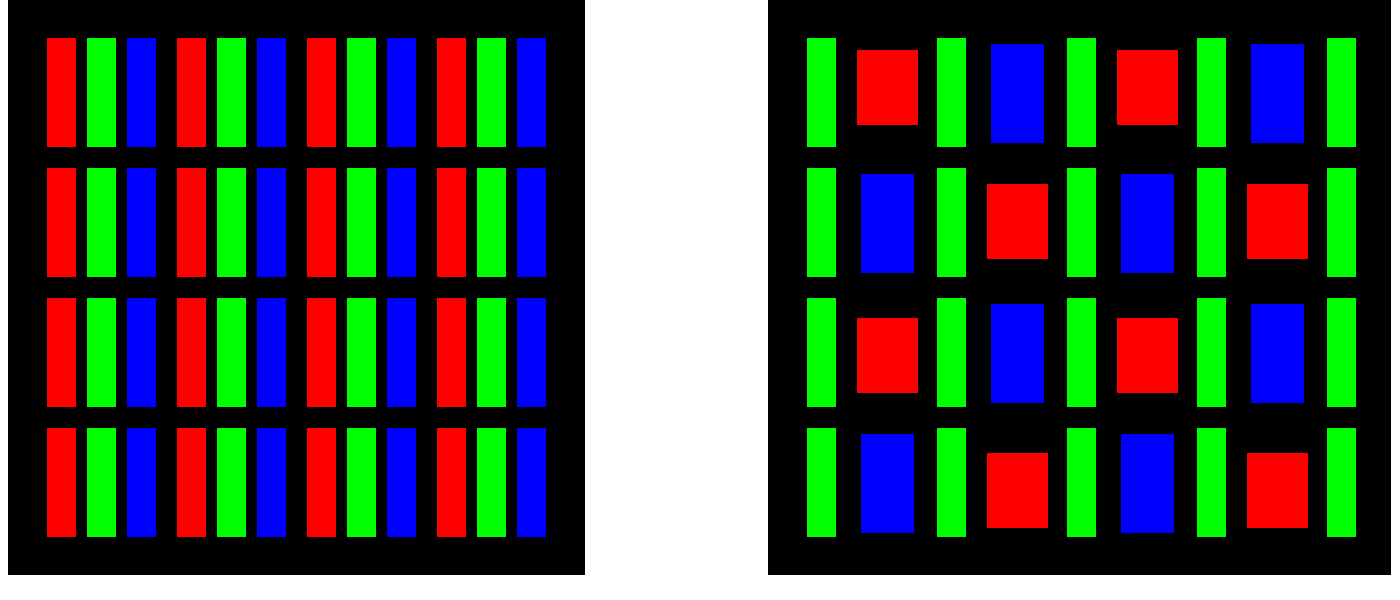
Subpixels may be arranged in different patterns, depending on the type of display. An LCD typically arranges its subpixels in a simple grid of three rectangular subpixels that form a square. Each one takes up an equal amount of space. OLED screens, on the other hand, will use other subpixel arrangements. For example, a PenTile arrangement is designed for adjacent pixels to share subpixels, allowing for the same effective resolution with fewer subpixels.
NOTE: Computers connected to LCD and OLED monitors can enable subpixel anti-aliasing. This is a method of anti-aliasing text that takes into account the arrangement of the subpixels on the screen to make the text sharper than monochrome anti-aliasing.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge