Telehealth
Telehealth is an umbrella term that encompasses health services provided using telecommunications technologies. It includes everything from the electronic delivery of patient health information and prescriptions to remote interactions between patients and doctors in different locations.
Telehealth has existed for decades, dating back to the invention of the telephone in the late 1800s. It first enabled doctors and nurses to communicate over long distances and provide medical information to their patients over the phone. The telephone provided a significant boost in medical care because patients were no longer limited by the expertise of doctors in their local area.
As technology has progressed, so has telehealth. For example, the fax machine made it possible to transfer medical information between hospitals in minutes instead of days. Pagers helped notify doctors and surgeons in emergency situations. Modern technologies like smartphones and the Internet make it possible for medical professionals and patients to access health information anytime, anywhere. Online services like MyChart and AthenaNet provide patients with direct access to their own health records, including test results, scans, and medications.
Remote Healthcare
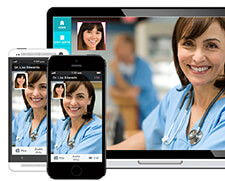
While telehealth encompasses many types of medical services, it is often used to describe remote healthcare. For example, a telehealth doctor may "visit" patients remotely using videoconferencing technology. Patients can book remote appointments and a doctor can evaluate their condition over the video feed. A more advanced type of telehealth, called telesurgery, allows doctors to perform remote surgery using a specialized robotic system.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge