UEFI
Stands for "Unified Extensible Firmware Interface."
UEFI is an interface that loads near the beginning of the boot sequence and provides custom configuration options for a PC. It is considered the successor to BIOS and offers many advantages, including mouse support, a graphical user interface, and support for 32-bit and 64-bit systems.
UEFI is a standardized version of the original Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) specification developed by Intel. It is managed by the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface Forum, comprised of more than 250 member companies. The standardized UEFI specifications are designed to ensure that components from different hardware manufacturers can be recognized and controlled via the UEFI.
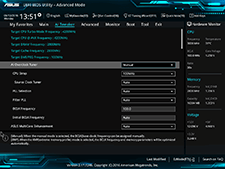
Accessing the UEFI
The UEFI is designed for advanced users, so by default it is not displayed during the startup process. The standard way to load the UEFI on most Windows PCs is to press the F2 key when the computer is starting up. Typically, you should press the key when the manufacturer's logo (such as "Dell" or "HP") appears. In Windows 8 and 10, you can also use the Troubleshoot option to enable "UEFI Firmware Settings" before the next restart.
Configuration options provided in the UEFI vary depending on the manufacturer and computer model. Typically, you can perform administrator tasks like formatting and partitioning storage devices. You may also be able to change your boot disk and activate or deactivate specific peripherals. Some systems even allow you to overclock your CPU or run your PC in a low-power "eco-friendly" mode.
NOTE: Intel-based Macs use EFI to manage the hardware configuration, but the UEFI is not available at startup.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge