Unified Memory Architecture
Unified Memory Architecture (abbreviated UMA) is a type of computer memory architecture that uses the same pool of memory for both the CPU and GPU. It is commonly used in computers with integrated graphics processors, as well as mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.
Computers with discrete graphics processing units have separate memory banks for the CPU and GPU. The CPU uses the main system RAM to store temporary data for applications and processes running on the computer, while GPUs use their own built-in memory banks of high-speed VRAM for image data. The PCI Express bus transfers data between the system RAM and the VRAM when necessary.
CPUs with an integrated GPU will share a single pool of memory between both processors, reducing the cost and complexity of the computer. This architecture eliminates the need to swap data between RAM and VRAM. In some cases, this results in slower performance as the CPU and GPU need to access memory over a bus that would otherwise only service the CPU.
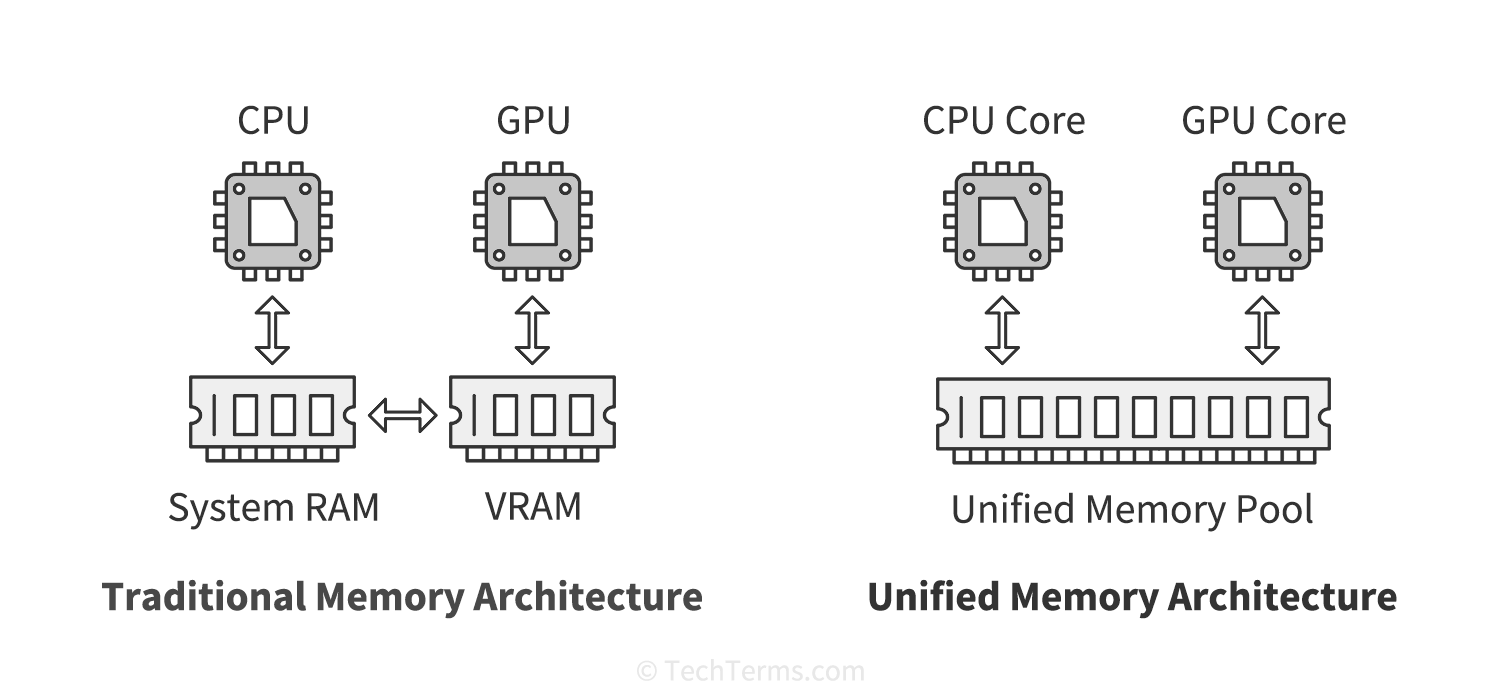
Apple introduced their implementation of a UMA with their M1 series of processors. Since these processors include the system's memory on the same system-on-a-chip as the CPU and GPU cores, they can access the shared memory pool at much higher bandwidth and with much less latency than other implementations. The CPU and GPU do not need to move data from one cache to another, and the data never has to leave the chip to go to a separate memory module.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge