SDN
Stands for "Software-Defined Networking."
SDN is a networking architecture that separates the responsibilities for routing and forwarding network data packets. A central server takes over all routing decisions for the network, instead of leaving those decisions up to each individual node. An administrator can configure and manage a network through software running on the server, instead of managing each device separately. Data centers, enterprise networks, and campuses often use SDN to manage large, complex networks.
Each function of a router or switch is conceptually part of one of three planes:
- The data plane (or forwarding plane) is responsible for the physical forwarding of data packets to the next node toward its destination.
- The control plane determines the routing of those data packets, creating a path of nodes for the packet to move along.
- The management plane configures the control plane by giving the network administrator access to a command-line interface or control panel.
In a traditional network infrastructure, each device is responsible for all three planes. In a software-defined network, each switch or node is only responsible for the data plane; the central server takes over the control and management planes.
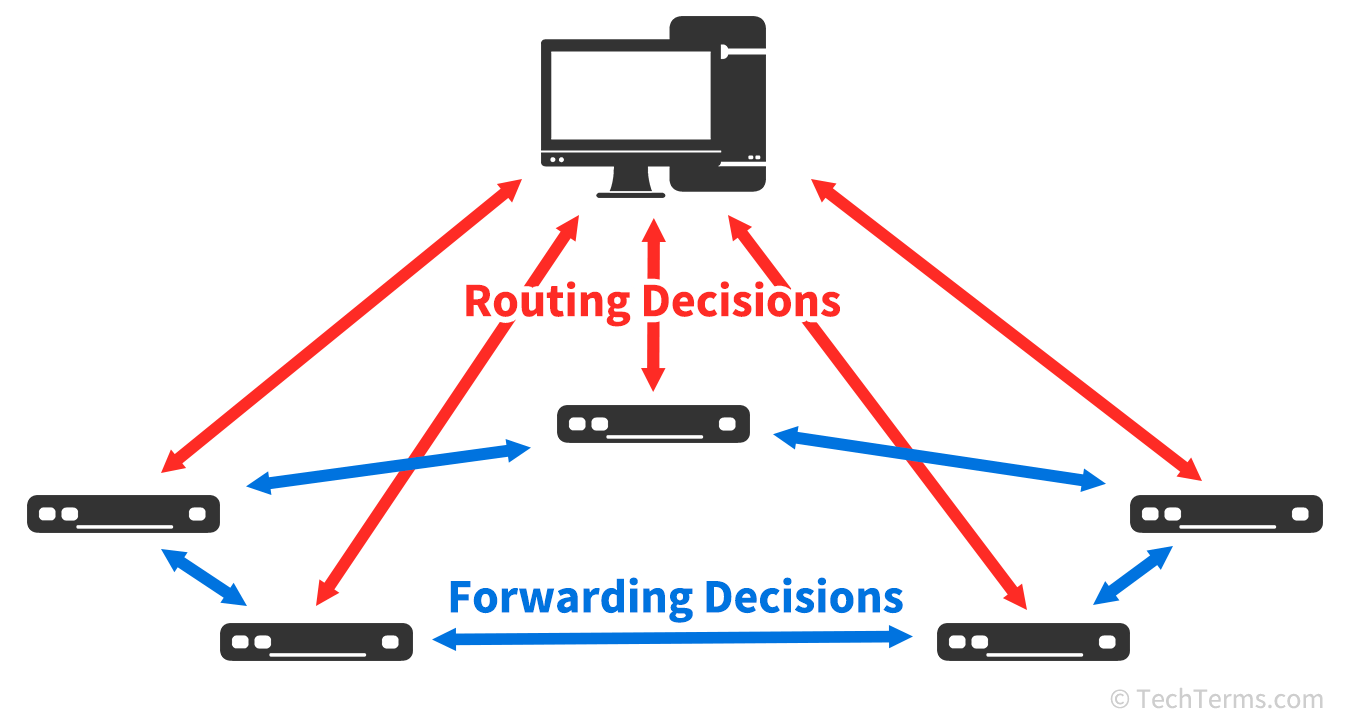
An administrator of a traditional network must configure each switch (or other type of node) on that network separately. A large network may have dozens or even hundreds of switches, which leads to a lot of duplicate work when updating configuration settings on each one. Software-defined networking centralizes the control and management of the entire network into a single dedicated device. An SDN server instructs the switches and other nodes how to forward data packets using a network protocol like OpenFlow.
In addition to being easier to manage, software-defined networks can move data more efficiently. Individual switches making routing decisions on their own may not choose the most efficient route, since they have limited knowledge of the conditions across the entire network. An SDN server, however, can monitor and control the entire network to optimize traffic for specific applications while bypassing congestion.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge