Wizard
A wizard is a part of an application's user interface that guides a user through several steps to complete a task. It takes a complicated process and breaks it into smaller steps, directing the user along and explaining each option. A wizard typically uses friendlier, more natural language than other interface elements to make it approachable for less-experienced users.
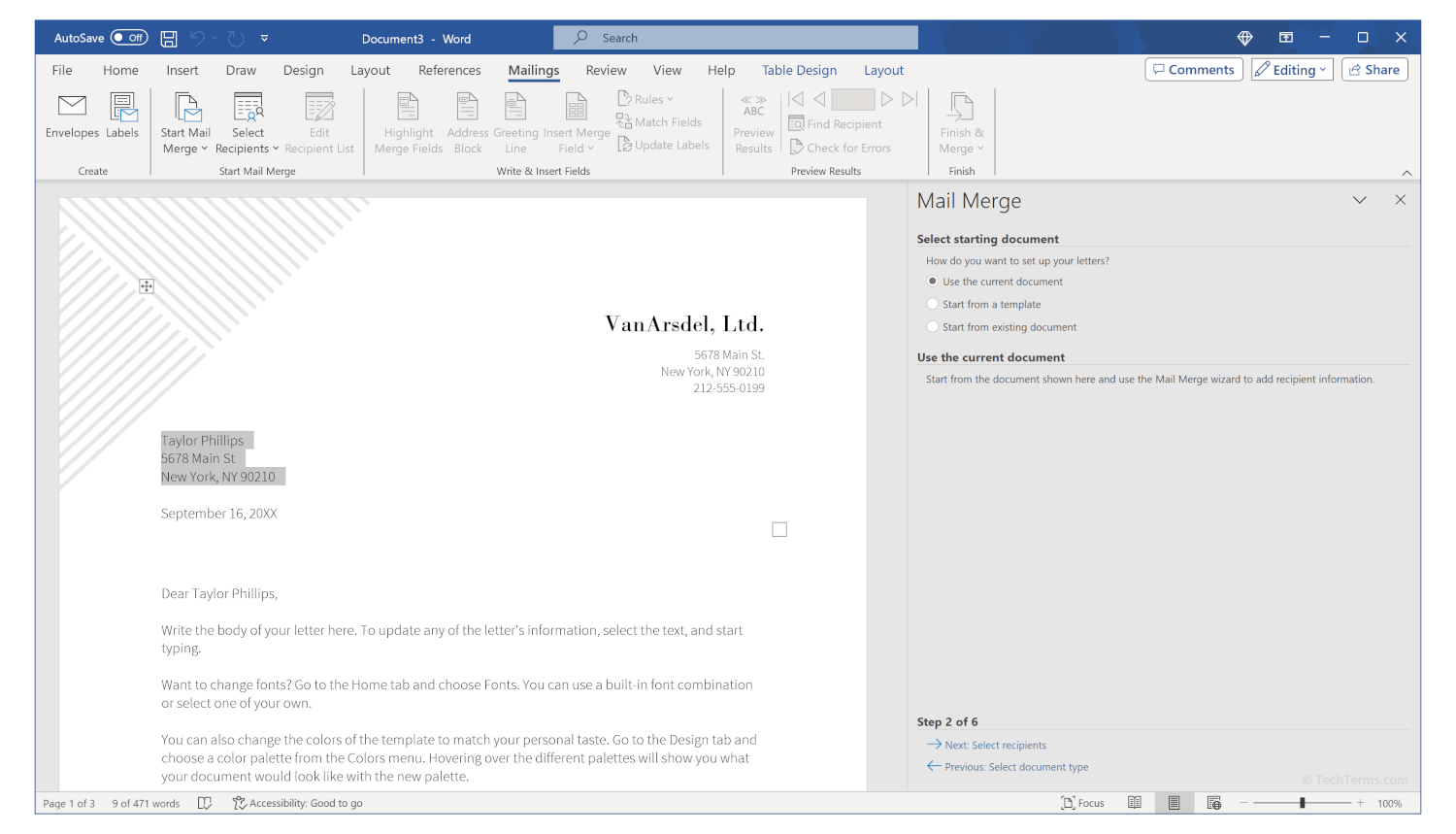
A typical wizard appears in a separate dialog box, sidebar, or other distinct part of an application window. It presents one option or setting at a time and provides context for that option to help you understand the result of each choice. It also lets you know how far along in the process you are, indicating which step you're on and how many steps remain. For example, Microsoft Word includes a Mail Merge wizard that helps guide you through automatically creating form letters using a database of contact information. It asks what type of document you want to make, has you select a list of recipients in a database or spreadsheet, then helps you write a letter by inserting automatic name and address information. It can even send the finished letters to the printer at the end. Experienced users can skip the wizard and do each step on their own, but the wizard ensures that you don't forget a necessary step and tailors each part towards the type of document you want to make.
Many types of software use wizards to help guide you through a task. Windows, macOS, and mobile operating systems use wizards (or assistants) to guide you through the installation process and set up options as you like. Application installers use them to let you select a destination folder and which features to include or exclude. Spreadsheet and database applications use wizards to guide you through data import and export options, and desktop publishing applications often use them to help you set up a document exactly how you want.
NOTE: The term "wizard" is most often associated with Windows and Windows applications, while other platforms like macOS and iOS use "assistant" instead.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge