Defragment
Defragmenting is a disk maintenance process that reorganizes the data on a hard disk to improve its performance. It identifies which files include fragmented data spread around the disk, then moves data around to improve read and write speed. Defragmenting hard disk drives is a common maintenance task, but it is unnecessary on SSDs and other flash drives.
When you save a new file to a hard disk, it breaks that data into small chunks on a disk platter called sectors. If the hard disk is relatively empty, it can easily allocate enough contiguous sectors to store the whole file in one spot. If you modify that file later in a way that takes up more space, and there aren't enough open sectors adjacent to it on the disk platter, the drive saves that data wherever there is room. Over time, files are broken up, or "fragmented," and scattered around all over the disk. Since the disk's read and write heads must move around more to read or write a file, this slows down disk access speeds and increases wear and tear on the disk drive.
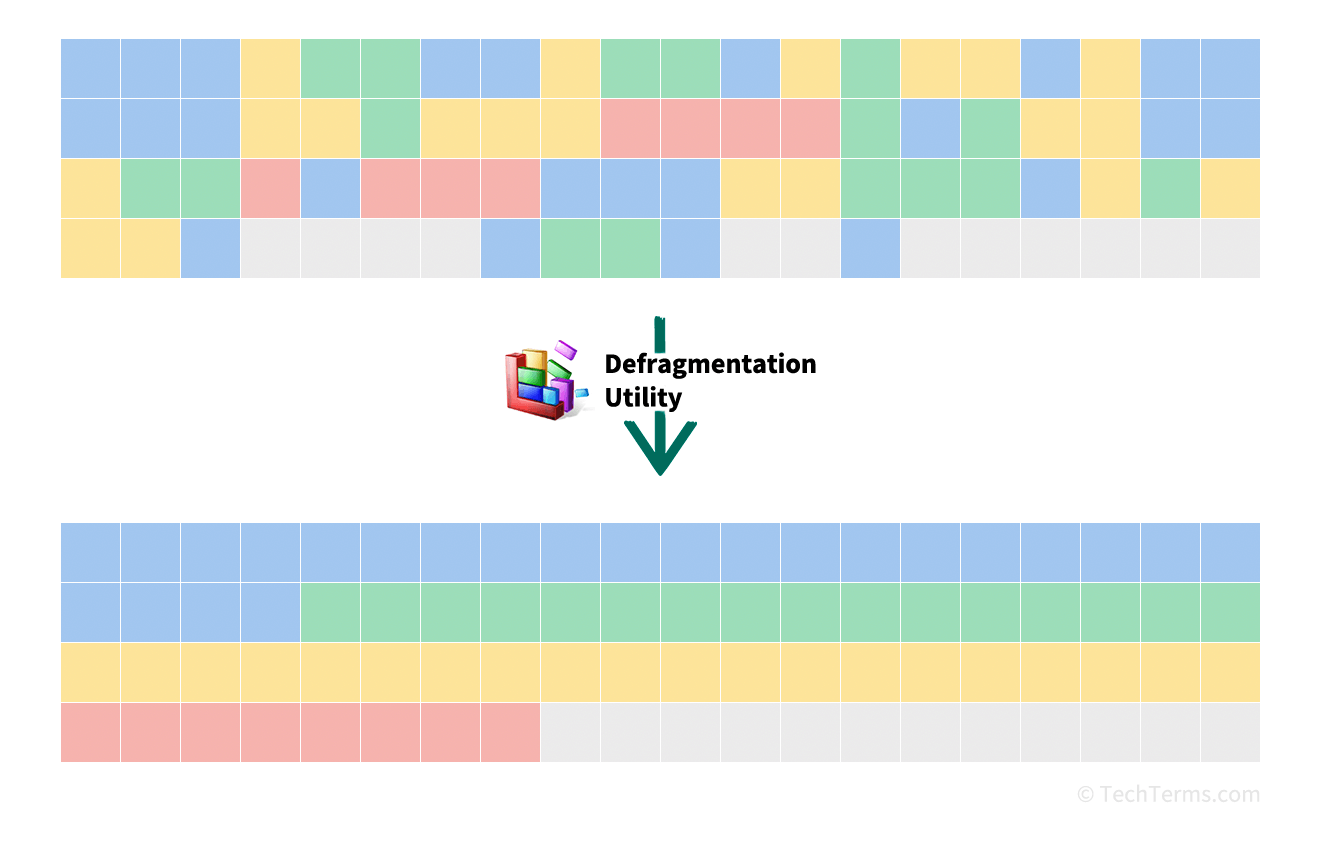
A defragmentation utility cleans up a drive in several steps. First, it scans the entire disk to create a map of sectors and tracks which file each sector is associated with. It then rearranges data to reunite fragmented files back into contiguous blocks. If a disk is very fragmented, defragmenting can recover disk space by consolidating data from partially-used sectors. Defragmentation can take a lot of time on large, heavily fragmented disks, so you should regularly defragment your hard drives. Windows and Linux both come with built-in defragmentation utilities that often run automatically. While macOS does not have its own defragmentation utility, it does include other features that minimize file fragmentation.
NOTE: While defragmenting a hard disk drive is considered regular maintenance, defragmenting a solid-state drive is unnecessary and often harmful. SSDs read and write data at the same speed regardless of whether a file is fragmented or not, and attempting to defragment an SSD may instead reduce its lifespan through excessive read and write cycles.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge