Volume
The word "volume" has several different meanings. In physics, it measures both sound and three-dimensional space. Audio volume defines the intensity of soundwaves, or how loud a sound is. Spacial volume describes how much space a three-dimensional object takes up. In the computer world, "volume" has an entirely different definition related to data storage.
A computer volume is similar to a book volume, or a single book in a series. It refers to a specific storage area, such as an HDD or SSD. It may also be a section within a storage device. Before a computer can access data from a volume, it must mount it first. Once a volume is mounted, the computer may read and write data, depending on the volume's permissions. Unmounting the volume prevents it from being accessed.
Containers vs Volumes vs Partitions
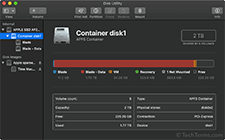
Some file systems, such as NTFS, use volumes as the top level of data storage. Others, such as Apple's APFS, use "containers." A single disk may have multiple containers. A container can store more than one volume and a volume may have multiple partitions. It is also possible for a storage device to have one container with a single volume that has one partition.
While a volume may contain multiple partitions, most file systems create separate volumes for each partition. Windows, for example, creates a new volume for each partition, labeling each volume with a letter, such as C:, D:, E:, etc. These volumes are also called "drives," even though they may not be separate physical drives.
NOTE: Since there is often a one-to-one relationship between volumes and partitions, these terms are also used interchangeably. However, a partition is technically part of a volume. For example, formatting a volume will erase all partitions contained in that volume.
 Test Your Knowledge
Test Your Knowledge